The Merge Won't Cut Gas Costs: 3 Money-Saving Tips.
As The Merger approaches, Ethereum-related topics are becoming more common, including discussions of post-Merger gas fees. The Ethereum Foundation has stated that the network's upcoming transitional PoS upgrade — The Merge — will not reduce gas fees. As specified by the Foundation:
Gas charges are a product of network demand versus network capacity. The Fusion deprecates the use of proof-of-work, moving to proof-of-stake for consensus, but does not significantly change parameters that directly influence network capacity or throughput.
The Merge won't change gas costs?
The Ethereum Merger aims to deprecate the use of proof of work, moving to proof of stake for consensus. However, this does not significantly change the parameters that directly influence network capacity or throughput.
It may be true that expensive gas fees have never stopped senior Ethereum users from engaging in the Ethereum ecosystem, which has a lot to do with their seniority in the cryptosphere. In the current bear market, the price of ETH stands at around $1,600, but ETH used to be very cheap: it only cost $0.4209 to buy one ETH in 2015.
The huge price gap gives senior crypto users who joined the space eight years ago a big advantage, as they hold a large amount of ETH. For them, the level of gas charges does not seem to be a major concern.
However, for ordinary Ethereum users and crypto newbies, expensive gas fees have always remained one of the obstacles preventing them from entering the Ethereum ecosystem . From July 2016 to May 2017, Ethereum transaction fees were between $0.01 and $0.10. However, on May 12, 2021, Gas' average fee reached $69 per transaction.
Gas costs: an obstacle for beginners?
Indeed, crypto newbies are hesitant to pay the gas fees required to participate in Ethereum-powered DeFi or GameFi projects, not only because the fees are high, but also because they are new to the ecosystem. crypto and therefore do not trust this ecosystem.
Therefore, most brands have a distinct marketing strategy to attract new users. For example, the famous SMS was once the most widely used messaging tool in the world. However, since 2019 WhatsApp has slowly replaced SMS in the UK, mainly because the former is free to use. Mobile service providers in the UK charge a rate of £0.07 to £0.11 for SMS usage.
Although these rates may not seem so high, as people use the tool more frequently and competitors start offering similar services at a lower price, these rates create a big barrier, which excludes more users.
This also applies to new users and new teams of developers in the cryptosphere.
Compared to paying expensive gas fees on Ethereum , people prefer to explore nascent ecosystems that are cheaper to operate, reflecting a normal decision to seek gain and avoid loss when people are faced with new choice.
READ MORE: Ethereum Merge Explained
Tips for saving gas costs
For retail investors, there are still several ways to reduce gas costs. We explain this to you in the sections below.
1 - Pay attention to network congestion and optimize your transaction hours
On Ethereum, transactions can peak on a certain date or time, driving up gas fees. If the transaction is not urgent, waiting for the network to cool down is a great way to save gas.
2 - Formulate trading strategies using tools
You can adopt tools to simulate an upcoming trade without actually executing the trade, allowing you to track and adjust the necessary gas charges before paying the charges.
For example, DeFi Saver is a great tool that helps you organize any type of Ethereum transaction and test and adjust your transactions by running simulation mode.
3 - Choose a blockchain with lower gas fees
Ethereum is not the only public chain available on the market. Given Ethereum's barrier to entry resulting from high gas fees, some users have been attracted to newer public chains due to their superior performance and lower fees.
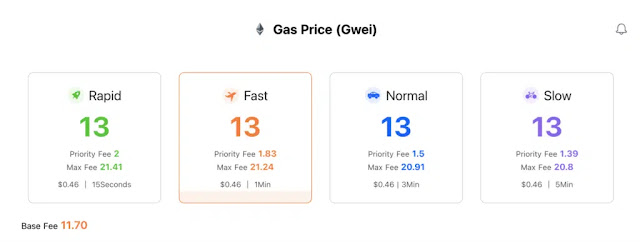
First, let's take a look at the current gas price of Ethereum. Currently, the normal gas fee on Ethereum is $0.46.
Here we recommend several other public channel ecosystems and also compare their gas fees.
BNB Chain
BNB Chain is a public blockchain developed by Binance, a leading cryptocurrency exchange. As an EVM-compatible chain, BNB Chain attracts users who are discouraged from using Ethereum due to expensive fees.
In addition, the public chain is also looking to strengthen its ecosystem and recruit more new users by tapping into BNB tokens. As shown in the figure below, BNB Chain is superior to Ethereum in terms of gas fees. On BNB Chain, the normal gas fee is 5.1 Gwei (about $0.03214).
CoinEx Smart Chain
Aiming to build an efficient DeFi system, CoinEx Smart Chain (CSC) is an EVM-enabled public chain built by CoinEx. As a global crypto platform committed to “making crypto trading easier”, CoinEx offers easy-to-use products and services and strives to introduce more new users to the blockchain industry by eliminating the obstacles to the cryptosphere space. CSC also uses PoS and is characterized by increased security and stability, high performance and low gas costs. On CSC, the normal gas price is only $0.01 (see image below).
Lower gas costs allow retail users, as well as new developer teams, to save substantial costs. The CSC is currently organizing the second global CSC hackathon, which offers a huge prize pool. Join the hackathon if you want to incubate a new project: https://cscchallenge.devpost.com/.
Huobi Ecological Chain
Huobi Ecological Chain (Heco) is a decentralized public chain offering efficient transactions and compatibility with smart contracts. Aiming to help developers at every stage of their growth, Heco strives to build a strong ecosystem with a closed loop from technology development to deal to app promotion. Under normal circumstances, Heco's gas charge is 2.6 Gwei (about $0.016385).
READ MORE: Ethereum: $2,000 After The Merge?








0 Comments